Which Covid-19 Vaccine?
- yihuilee

- Jul 29, 2021
- 3 min read
Updated: Aug 21, 2021

Covid-19 vaccination in Malaysia
To date, our vaccination rate in Malaysia has achieved an encouraging 400,000 doses per day and most states have had more than 20% of the population getting at least the first dose. (1)
Currently, the three covid-19 vaccines given by the Ministry of Health Malaysia are Comirnaty (Pfizer-BioNTech), Vaxzevria (Oxford-Astrazeneca) and CoronaVac (Sinovac). As people are not allowed to choose which of the three vaccines that are given, concerns and worries arisen, mainly due to inadequate information on the efficacy and safety of the vaccines offered. The emergence and dominance of the B.1.617.2 (delta) variant of the Covid-19 virus which is reported to be more transmissable further complicate the global recovery course and leave no room for vaccine-hesitancy. Hence, healthcare professionals are responsible to give the best evidence-based advice regarding covid-19 vaccination to the people.
Comparison of the vaccines against variants of concern
A head-to-head comparison of all three above stated vaccines is unavailable, however, based on a few studies, we can have a quick understanding of how these vaccines fair against each other and the various variants, including the notorious delta variant.
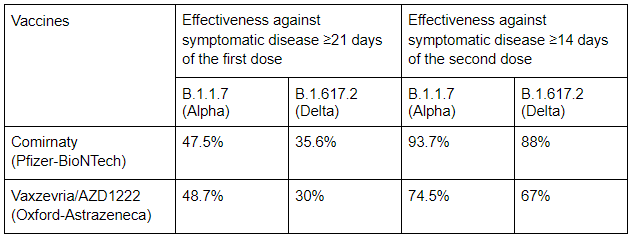
The following results are based on the study conducted by Public Health England, with data extracted from October 2020 to May 2021 to evaluate the effectiveness of vaccines against the Delta variant. Both vaccines were found to have lower effectiveness against the delta variant compared to the alpha variant, and completion of the second dose increase the effectiveness tremendously. (2)
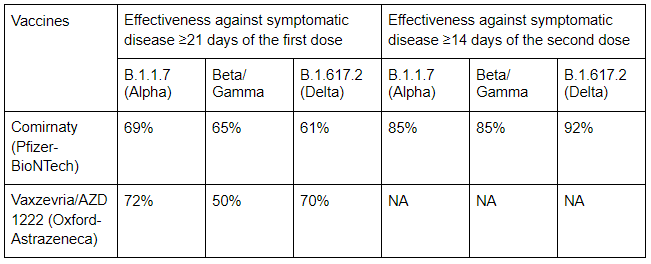
Another preprint report of the study conducted in Canada from December 2020 to May 2021, evaluated the effectiveness of vaccines against variants of concerns gave the results as below. Do bear in mind that this report has not been peer-reviewed and should not be used to guide clinical practice. Data for effectiveness after the second dose was only available for Comirnaty (Pfizer-BioNTech). (3)
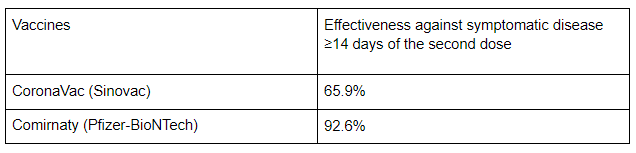
The only head-to-head comparison between CoronaVac (Sinovac) and Comirnaty (Pfizer-BioNTech) can be found in a study conducted in Chile from February to May 2021. The study was aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of Coronavac (Sinovac) which is the mainstay of vaccination strategy in the country. As the estimation of Comirnaty (Pfizer-BioNTech) effectiveness was presented in the Supplementary Appendix, comparison with Coronavac (Sinovac) is made possible. Comirnaty (Pfizer-BioNTech) was found to be more effective among these two vaccines. However, the delta variant was not the variant of concern detected in Chile during the study period and hence no data for comparison was available. (4)
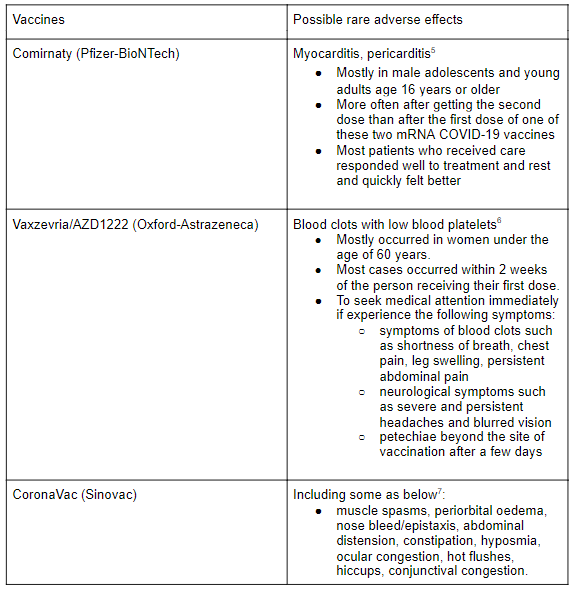
Possible rare adverse effects
Some of the rare adverse effects are listed for the three vaccines used in Malaysia. (5, 6, 7)
Take home message
As Covid-19 vaccines are still considered new in the market and healthcare experts globally are still evaluating the effectiveness and safety data through either well-designed studies or post-marketing surveillance. Up-to-date, healthcare professionals may not be able to give definite answers to questions such as which vaccine is the best for a certain variant or population and which vaccine is the safest for a particular group of people. Policymakers globally can only make vaccine procurement decisions based on the best available clinical data, financial resources, availability of vaccine supplies, etc.
The best vaccine is the readily available one, and it’s imperative to complete the full doses according to the recommended dosing schedule for a maximum protection.
References
The Special Committee On Covid-19 vaccine SUPPLY (JKJAV). https://www.vaksincovid.gov.my/en/. Accessed July 28, 2021.
Lopez Bernal J, Andrews N, Gower C, et al. Effectiveness of Covid-19 Vaccines against the B.1.617.2 (Delta) Variant [published online ahead of print, 2021 Jul 21]. N Engl J Med. 2021;10.1056/NEJMoa2108891. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2108891
Nasreen S, Chung H, He S, et al. Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines Against variants of concern in Ontario, Canada. medRxiv. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.06.28.21259420v2.full. Published January 1, 2021. Accessed July 28, 2021.
Jara A, Undurraga EA, González C, et al. Effectiveness of an Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine in Chile [published online ahead of print, 2021 Jul 7]. N Engl J Med. 2021;NEJMoa2107715. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2107715
Myocarditis and Pericarditis Following mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/safety/myocarditis.html. Accessed July 29, 2021.
AstraZeneca's COVID-19 VACCINE: EMA finds possible link to very rare cases of unusual blood Clots with low platelets. European Medicines Agency. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/astrazenecas-covid-19-vaccine-ema-finds-possible-link-very-rare-cases-unusual-blood-clots-low-blood. Published April 8, 2021. Accessed July 29, 2021.
Assakina L. Frequently Asked Questions (faq) about Covid-19 Vaccine. National Pharmaceutical Regulatory Agency (NPRA). https://www.npra.gov.my/index.php/en/component/content/article/82-english/announcement-main/1527195-faq-biologics.html?Itemid=1391. Published July 14, 2021. Accessed July 29, 2021.






Comments